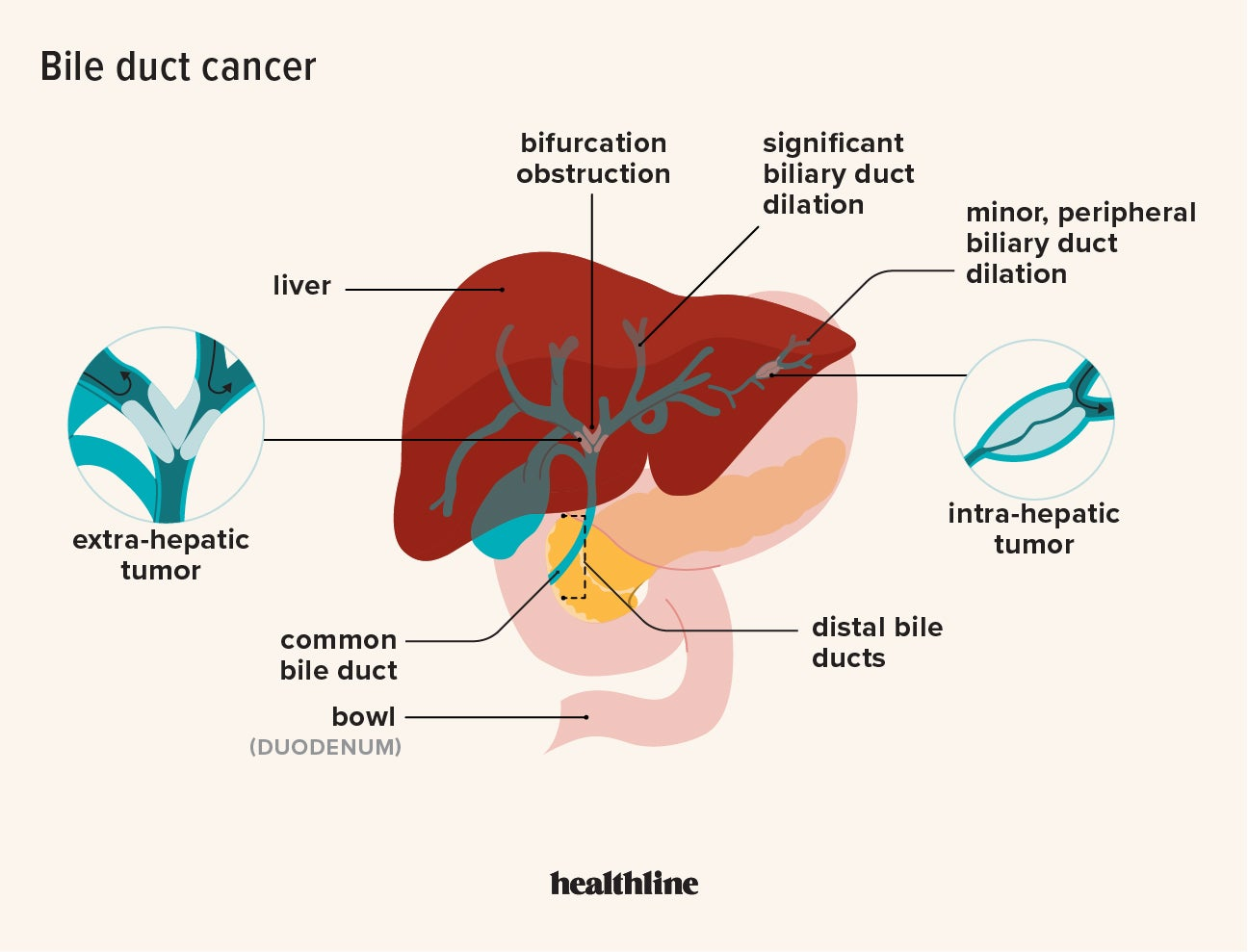
Bile imbalance liver cancer represents a critical intersection between metabolic dysfunction and oncogenesis in the liver. Recent research has unveiled the profound implications of disrupted bile acid metabolism, linking it to liver cancer development, particularly hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). This innovative study highlighted a pivotal molecular switch that may offer new pathways for effective liver cancer treatment, emphasizing the need for deeper understanding of liver disease causes. As bile acids are vital for digestion and play a role in metabolic regulation, their imbalance can set off a cascade of inflammatory processes leading to cancer. By targeting pathways like YAP FXR signaling, scientists aim to enhance therapeutic strategies that could address the rising incidence of liver cancer.
The relationship between bile acid dysregulation and liver malignancies is gaining attention in contemporary medical research. When the delicate balance of bile production in the liver is disrupted, it can result in severe health implications, including the emergence of liver tumors. Advancing our knowledge on hepatocellular carcinoma and related liver conditions has led to promising investigations into new therapeutic interventions. The role of bile acids not only aids in digestion but is also pivotal in maintaining metabolic homeostasis, which, when disrupted, paves the way for chronic liver diseases. Insights into YAP and FXR signaling offer a beacon of hope for developing innovative liver cancer treatments that target the underlying mechanisms of bile metabolism.
Understanding Bile Acid Metabolism in Hepatic Health
Bile acid metabolism plays a crucial role in maintaining liver health and overall metabolic functions in the body. Bile acids are not just responsible for fat digestion; they also act as signaling molecules that regulate various biological pathways, which are essential for liver homeostasis. The liver synthesizes bile acids from cholesterol, and this complex process is tightly regulated to prevent harmful imbalances. Disruption in bile acid metabolism can lead to a range of liver diseases, including fibrosis, cirrhosis, and hepatocellular carcinoma, thus highlighting the importance of this metabolic pathway in hepatic health.
Research has shown that disturbances in bile acid homeostasis can trigger chronic liver injury and inflammation, which are significant risk factors for developing liver cancer. When bile acid levels rise excessively due to metabolic dysregulation, they can cause cellular toxicity and initiate a cascade of inflammatory responses. Understanding the intricate dynamics of bile acid metabolism is vital for identifying potential therapeutic targets for liver cancer and other liver diseases, making this area a focal point in current liver biology studies.
The Role of YAP FXR Signaling in Liver Disease
YAP (Yes-associated protein) plays a pivotal role in liver disease, especially in relation to bile acid metabolism. The relationship between YAP and FXR (Farnesoid X receptor) is significant because FXR is crucial for maintaining bile acid homeostasis. When YAP is overactive, it inhibits FXR function, leading to an overproduction of bile acids. This imbalance results in liver inflammation and the potential progression to liver cancer. Research has indicated that by targeting YAP or enhancing FXR activity, researchers can help restore normal bile acid levels and mitigate liver injury.
The Hippo pathway, which regulates YAP activity, is essential for controlling liver cell growth and metabolism. Dysregulation of the Hippo/YAP signaling pathway has been associated with numerous types of cancers, including hepatocellular carcinoma. Therefore, understanding how YAP modulates bile acid metabolism opens up new avenues for liver cancer treatment. Therapies that inhibit YAP’s activity or activate FXR may not only reduce bile acid accumulation in the liver but also prevent the onset of cancerous changes in hepatocytes.
Exploring Liver Cancer Treatments Targeting Bile Imbalance
The identification of bile imbalance’s role in liver cancer has prompted innovative research into targeted therapies. With findings indicating that restoring normal bile acid levels could potentially halt cancer progression, several therapeutic strategies are being explored. For instance, pharmacological agents that activate FXR could promote bile acid excretion and improve liver function, thus reducing the risk of hepatocellular carcinoma. Additionally, inhibitors of YAP could also represent a promising treatment avenue by restoring the normal balance of bile acids and counteracting liver inflammation.
Current studies are focused on developing drugs designed to enhance FXR activity, as activation of this nuclear receptor has been shown to decrease liver damage effectively. In this context, researchers are also investigating compounds that can inhibit HDAC1 to alleviate the suppressive effects of YAP. These pharmacological approaches have the potential not only to treat existing liver damage but also to prevent the onset of liver diseases associated with bile metabolism disruptions, making them crucial candidates in the evolving landscape of liver cancer treatment.
Challenges in Liver Disease Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma often poses significant challenges due to the insidious nature of its symptoms. Many patients remain asymptomatic until the disease reaches advanced stages, making early detection critical. Traditional diagnostic tools may not always accurately pinpoint the underlying causes of liver problems, such as bile imbalance. As a result, researchers are advocating for more sensitive diagnostic methodologies that could facilitate early identification of liver conditions, thereby enhancing treatment outcomes.
Treatment of liver diseases relies heavily on accurately diagnosing underlying causes, including bile acid metabolism issues. Traditional treatments often focus on managing symptoms rather than addressing the root causes of liver dysfunction. The development of more targeted therapies aimed at correcting bile imbalances, however, points to a future where liver disease might be treated more effectively. By focusing on the molecular mechanisms that lead to liver cancer, healthcare providers will be better equipped to implement preventative measures and tailor treatments that address the specific metabolic disruptions in patients.
The Synergy of Future Research and Clinical Applications
As research into bile acid metabolism and its link to liver cancer progresses, the potential for clinical applications continues to grow. The findings from recent studies highlight the need for further exploration into how specific pathways, like YAP and FXR signaling, interact with liver cancer development. By understanding these mechanisms, researchers can develop targeted therapies that not only treat liver cancer but also prevent its occurrence by restoring metabolic balance within the liver.
Furthermore, interdisciplinary collaborations between molecular biologists, oncologists, and clinicians are vital for translating these laboratory findings into practical treatments. Innovations in drug development, such as small molecule inhibitors or gene therapies that specifically target bile acid pathways, may lead to groundbreaking advancements in liver cancer care. The ongoing dialogue between research findings and clinical practice can enhance our understanding of liver disease and improve patient outcomes significantly.
Impact of Lifestyle on Liver Health and Bile Acid Regulation
Lifestyle factors significantly influence liver health and the regulation of bile acids. Diet, exercise, and alcohol consumption play pivotal roles in determining the body’s metabolic state and can either exacerbate or mitigate liver issues. A diet high in saturated fats and sugars can lead to an overload of bile acids, contributing to liver damage over time. Conversely, adopting a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats, along with regular physical activity, can promote bile acid homeostasis and improve overall liver function.
Additionally, excessive alcohol intake is a well-documented risk factor for liver disease, leading to inflammation and ultimately liver cancer. Public health initiatives focused on educating populations about the importance of a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the prevalence of liver diseases linked to bile imbalance. Lifestyle modification remains a practical, preventative approach that can significantly impact liver health long before clinical symptoms arise, emphasizing the importance of proactive measures in the community.
Innovative Therapies in Liver Cancer Research
The quest for innovative therapies in liver cancer continues, with a growing focus on molecules that can modulate bile acid metabolism. Recent studies have opened avenues for the development of drugs that can specifically target pathways involved in bile production and metabolism, such as the FXR and YAP signaling pathways. These emerging treatments aim to correct bile acid imbalances that contribute to liver damage and cancer progression, offering hope for patients with hepatocellular carcinoma.
Clinical trials are underway to assess the effectiveness of these innovative therapies, potentially marking a significant shift in liver cancer management. By targeting the underlying metabolic disturbances that predispose individuals to liver disease, researchers are optimistic about improving treatment outcomes and reducing the overall burden of liver cancer. The integration of these new therapies into standard treatment protocols could revolutionize how we approach liver cancer care.
The Importance of Early Intervention in Liver Cancer
Early intervention in liver cancer is pivotal for improving survival rates and treatment success. Given that hepatocellular carcinoma often develops silently and is typically diagnosed at later stages, proactive screening for individuals at high risk is essential. Strategies focusing on regular monitoring of patients with known liver diseases, particularly those associated with bile imbalance, can facilitate earlier detection and timely treatment. By identifying liver cancer in its initial stages, healthcare providers can implement more effective therapeutic interventions.
Moreover, education on recognizing early signs of liver disease is crucial for prompting individuals to seek medical attention sooner. Increasing public awareness regarding risks associated with bile acid dysregulation, including lifestyle factors that contribute to liver cancer, can drive more patients towards preventative care. Integrating educational campaigns with regular screenings can create a comprehensive approach to tackle the increasing incidence of liver cancer, reducing healthcare burdens while improving patient outcomes.
Addressing Bile Imbalance and Liver Health through Research
Continued research into the mechanisms behind bile imbalance and its link to liver health is fundamental for developing new treatments. The liver’s intricate role in synthesizing bile acids makes it a key player in various metabolic pathways. As studies delve deeper into the genetic and molecular factors influencing bile acid production and regulation, significant insights can emerge that inform clinical practice. Innovations in research methodologies, including genome editing and bioinformatics, will bolster our understanding of liver disease and its nuances.
Furthermore, collaborative efforts among researchers, clinicians, and public health officials will enhance the translation of scientific discoveries into effective treatments and preventative measures. Establishing research partnerships focused on liver health can lead to rapid advancements in identifying pathways that contribute to liver cancer. By prioritizing this research, we not only improve the understanding of liver diseases but also provide a pathway towards effective strategies for managing and preventing liver cancer in the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
How does bile imbalance contribute to liver cancer development?
Bile imbalance can lead to an overproduction of bile acids, resulting in liver injury, inflammation, and ultimately hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), the most common form of liver cancer. Disruption in bile acid metabolism, primarily regulated by the FXR receptor, can trigger these damaging processes.
What role does YAP play in bile acid metabolism and liver cancer?
YAP (Yes-associated protein) is crucial in regulating bile acid metabolism. In liver cancer, YAP can disrupt FXR function, leading to an imbalance in bile acids, which promotes tumor formation and HCC progression by causing liver inflammation and fibrosis.
What are some potential treatments for liver cancer linked to bile acid metabolism?
Potential liver cancer treatments involve stimulating FXR function to restore bile acid homeostasis and reduce liver damage. Enhancing bile acid excretion or inhibiting proteins like HDAC1, which enable YAP’s repressive effects, are promising approaches to disrupt the cycle of liver injury and cancer.
Can targeting FXR influence liver disease outcomes related to bile imbalance?
Yes, targeting FXR is a promising strategy in managing liver disease linked to bile imbalance. By enhancing FXR activity, it may be possible to correct bile acid metabolism, reduce liver inflammation, and slow down the progression of liver cancer such as hepatocellular carcinoma.
What are the underlying causes of bile imbalance and its connection to liver disease?
Bile imbalance can arise from various factors including genetic mutations, dietary influences, and liver diseases that affect bile acid production. This imbalance is closely tied to liver disease causes, as it can lead to inflammation and increase the risk of developing liver cancer.
Are there any experimental models studying bile imbalance and liver cancer?
Yes, recent studies have utilized experimental models to analyze the relationship between bile imbalance and liver cancer. These models focus on how YAP activity and FXR regulation impact bile acid metabolism, offering insights into potential therapeutic strategies for hepatocellular carcinoma.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Bile Imbalance | Crucial to liver health, bile acids help digest fats and regulate metabolic processes. |
| Link to Liver Cancer | Disruption in bile acid production can lead to liver diseases, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). |
| Key Findings | YAP, a molecular switch, represses FXR, resulting in increased bile acid production and liver damage. |
| Therapeutic Implications | Potential treatments may involve enhancing FXR function or promoting bile acid excretion to prevent liver cancer. |
| Research Support | Study funded by the National Institutes of Health and National Cancer Institute, focusing on liver biology and cancer. |
Summary
Bile imbalance linked to liver cancer is a significant finding in current medical research. The recent study highlights how disruptions in bile acid production can initiate liver diseases such as hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). By identifying the role of the YAP molecular switch in regulating bile acid metabolism, researchers pave the way for innovative treatment methods that may effectively combat liver cancer. This insight could lead to therapies that prevent bile acid accumulation and the interplay between hormonal regulation and cancer pathology, emphasizing the importance of maintaining bile balance for liver health.