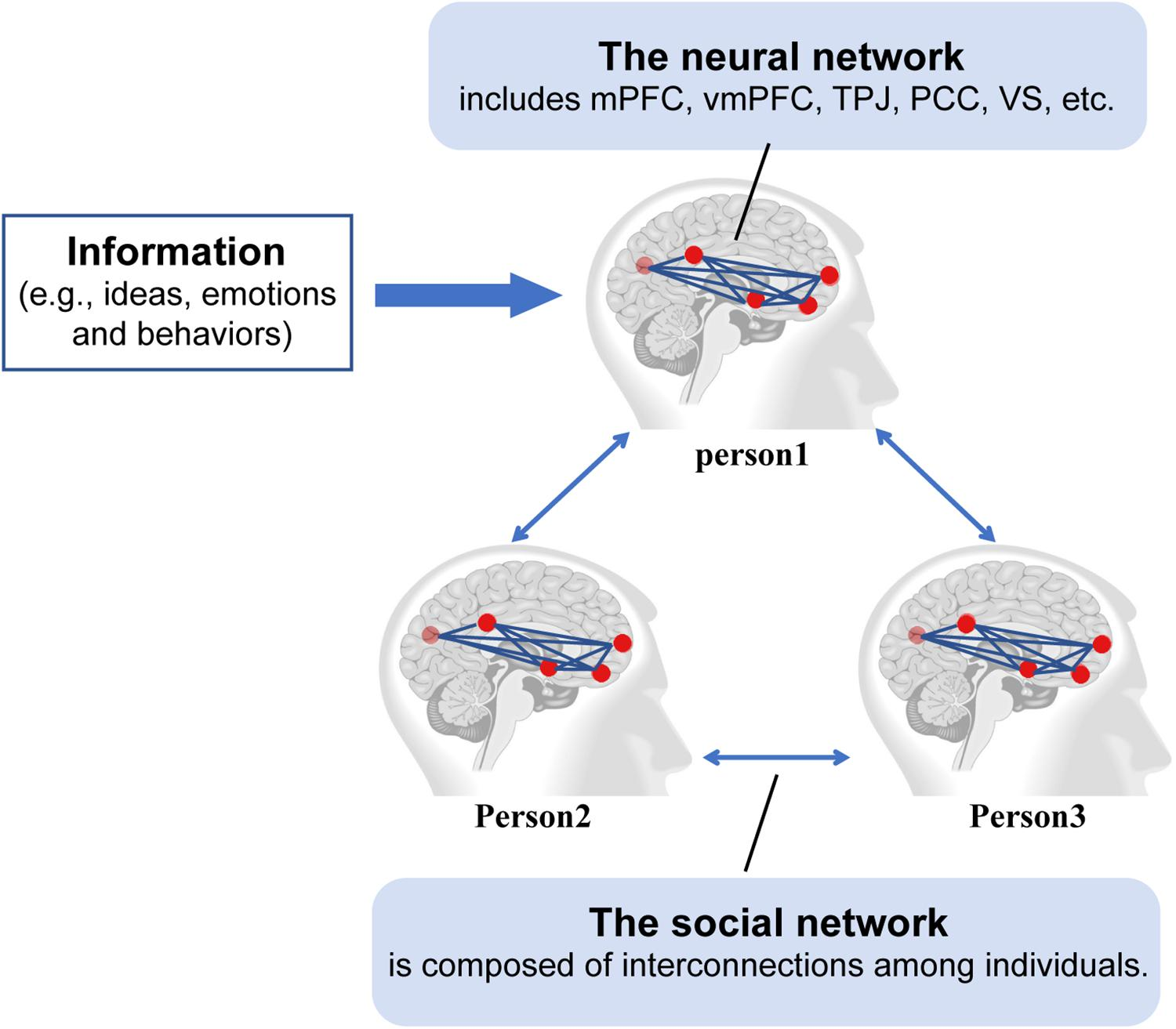
Social connection neuroscience is emerging as a pivotal field of study, uncovering the intricate ways our brains interpret social interactions akin to basic human needs like food and water. Recent findings highlight the neurological basis of social needs, showcasing how vital these connections are for both mental health and social behavior. Research indicates that social isolation can severely impact emotional well-being, further underscoring the importance of understanding the hypothalamus function in regulating our interactions. Moreover, the detrimental effects of loneliness on health are gaining recognition, positioning social connection neuroscience as an essential area for exploration in modern health discussions. As we delve deeper into the systems that drive our desire for social engagement, we gain crucial insights into the mechanisms behind our collective experiences.
The field of social neuroscience is focused on unraveling the underlying mechanisms that drive our need for interaction with others. This area explores the neurological frameworks that account for our social preferences, including examining the brain’s role in our responses to social stimuli. With mental health being closely tied to our ability to connect, understanding the brain’s circuitry involved in social behavior can provide clarity on issues related to social isolation and loneliness. Furthermore, by investigating how our brain’s regulatory systems, like the hypothalamus, function concerning social needs, researchers aim to uncover how these dynamics influence our overall well-being. Thus, the exploration of social connection from a neuroscientific perspective could reveal essential insights into fostering healthier social environments.
The Importance of Social Connection in Health
Social connection has increasingly been recognized as a vital element for overall health and wellbeing. Research shows that just like basic physical needs such as food and water, social interactions are crucial for maintaining mental health. Health professionals are sounding the alarm about social isolation, especially in younger populations who may be suffering silently due to a lack of meaningful social connections. Studies indicate that social isolation can lead to various psychological issues, including anxiety and depression, causing a significant impact on one’s overall mental health.
This growing body of research underscores the notion that our brains are wired to seek social engagement. Specifically, the neurological basis for these needs is becoming clearer, as scientists investigate the interconnected systems that prompt individuals to seek companionship. Understanding these mechanisms not only sheds light on why we form social bonds but also highlights the potential dangers of neglecting our social health.
Neuroscience of Social Isolation
The neurological basis of social isolation is a topic that has garnered considerable interest in recent years. Researchers are focusing on the hypothalamus, a brain region that plays a critical role in regulating both social behavior and physiological needs. This understanding has emerged from studies indicating that the brain’s response to social isolation can mimic the feelings of deprivation associated with hunger or thirst. Such findings suggest that social needs are not merely emotional; they are deeply embedded in our neurological frameworks.
Recent studies demonstrate how prolonged isolation can lead to aversive states in the brain, inhibiting one’s ability to engage in social interactions over time. For instance, experiments on mice indicated that extended periods of loneliness could lead to a dislike for social interactions. This finding poses significant implications for human behavior, as it suggests that as individuals experience more isolation, their capacity for social interaction diminishes, exacerbating issues of loneliness.
Understanding the Hypothalamus and Social Behavior
The hypothalamus is central to understanding the complex relationship between our neurological functions and social needs. This small but powerful region of the brain regulates various drives, including hunger, thirst, and even the desire for social interaction. Researchers, including those at Harvard, have shown that neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during social deprivation phases, underscoring its role in regulating our social appetites much like our physical needs for food and water.
Furthermore, examining how the hypothalamus interacts with other regions of the brain provides insight into how social behaviors are linked to overall health. It reveals that social connection is intertwined with our neurological makeup, and disruptions to this connectivity can lead to significant mental health challenges. This lines up well with existing literature that points to the need for community and interaction as fundamental human experiences essential for psychological stability.
The Impact of Loneliness on Health
Loneliness is not just an emotional state; it carries significant repercussions for physical health. Numerous studies have linked feelings of loneliness with various health issues, from cardiovascular diseases to a weakened immune response. The recent emphasis on mental health has highlighted how persistent loneliness can lead to chronic stress, which, in turn, affects bodily functions and overall wellbeing.
Understanding the impact of loneliness extends to recognizing how it influences social behavior. Individuals suffering from prolonged loneliness may withdraw from social settings, which can perpetuate a cycle of isolation and lead to further health complications. As experts investigate these patterns, it becomes clear that tackling loneliness is not merely about enhancing social interactions, but also about protecting and improving physical health.
Sensory Inputs and Social Needs
Recent findings have revealed that sensory inputs are critical to fulfilling our social needs. In experimental setups, mice that were isolated but still able to see and hear their companions displayed similar feelings of loneliness as completely isolated mice. This emphasizes the importance of multi-sensory experiences in maintaining social engagement and emotional wellbeing. Tactile stimulation, in particular, seems to play an essential role, indicating that our experiences of social connection deepen through physical interactions.
For humans, the implications of these studies can be profound. The physical contact we share with loved ones is an integral aspect of social behavior, offering comfort and reinforcing bonds. In the age of digital communication, understanding the need for physical touch and presence can inform strategies to combat loneliness and enhance our social experiences. As researchers continue to explore these dimensions, the focus on sensory elements will remain a vital component of understanding social connection.
Restoring Social Engagement in a Digital Era
As society navigates an increasingly digital landscape, the challenge of maintaining social connections becomes more pressing. The reliance on virtual interaction raises concerns that it may not fulfill the fundamental human needs for touch and presence. Studies are beginning to show that while technology offers new avenues for communication, it cannot wholly replace meaningful physical interactions that contribute significantly to mental health and social behavior.
In addressing the rising levels of social isolation, communities are exploring ways to enable face-to-face interactions that foster genuine connections. Initiatives aimed at creating more opportunities for social engagement, such as community events or activities centered on physical participation, are essential. These grassroots efforts can play a critical role in reversing trends of loneliness and promoting a healthier social environment.
Social Bonds and Mental Health
The profound link between social bonds and mental health has been underscored by recent research initiatives. Findings suggest that strong social connections can act as protective factors against mental illness, enhancing resilience in the face of stress and adversity. Conversely, the absence of these connections can lead to detrimental effects on mental health, manifesting as anxiety, depression, or other challenging psychological conditions.
Understanding this dynamic is crucial not only for individual wellbeing but also for public health policies aimed at mental health promotion. By fostering environments that encourage social interaction, health professionals can mitigate the impacts of social isolation and contribute to improved mental health outcomes across communities. Recognizing the intrinsic value of social relationships can drive efforts to nurture these connections in various settings.
Research Insights into Social Behaviors
Ongoing research into social behaviors and their underlying neuroscience is providing critical insights into why human relationships are vital. By examining the neural mechanisms that influence social interactions, scientists are uncovering potential treatments for social disorders and mental health issues. This research is tapping into significant areas such as the neurological basis of social needs and the effects of social isolation.
As these studies progress, they illuminate pathways toward understanding complex social behaviors and how they relate to overall health. Insights gained from this field may not only transform how we view social relationships but also inform interventions aimed at enhancing social connectivity and mental health support across populations.
Navigating the Future of Social Interactions
As we look to the future, the challenge lies in balancing the benefits of technology with the profound need for meaningful social interactions. Innovations in communication tools must prioritize features that foster genuine social connections while also encouraging face-to-face interactions that are essential for emotional fulfillment. Addressing the mental health crisis precipitated by social isolation will require a proactive approach that emphasizes not just virtual connectivity but also physical presence.
Ultimately, navigating this landscape will necessitate a concerted effort from individuals, communities, and policymakers alike. By fostering environments that encourage authentic connections, society can work towards revitalizing the social fabric that is so crucial for mental health and overall wellbeing.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the connection between social isolation and neuroscience?
Social isolation can significantly impact mental health, with neuroscience revealing the underlying mechanisms of this phenomenon. Researchers have identified that the brain encodes social needs similarly to physiological needs, indicating that social isolation may trigger neurological responses akin to hunger or thirst, emphasizing the necessity of social connections for overall well-being.
How does the hypothalamus function in relation to social needs?
The hypothalamus plays a crucial role in regulating social needs by controlling the neural circuits that govern behaviors related to social interactions. Studies suggest that neurons in the hypothalamus are activated during periods of social deprivation, reflecting the brain’s response to social isolation and the intrinsic need to seek companionship.
What are the neurological bases of social needs?
Research highlights that the neurological bases of social needs involve specific neural circuits similar to those governing other essential needs like food and water. The studies suggest that the desire for social connection is driven not just by the pleasure it brings but also by the aversive feelings of loneliness, indicating a complex interplay between social behavior and brain function.
How does loneliness impact mental health through neuroscience?
Loneliness has profound effects on mental health, as neuroscience research shows it can alter brain function and increase susceptibility to mental health disorders. The neurological underpinnings of social isolation indicate that a lack of social interaction affects brain circuits associated with emotional regulation and stress responses, thereby exacerbating conditions like depression and anxiety.
What role does touch play in social connection neuroscience?
Touch is a vital aspect of social interaction that is deeply rooted in neuroscience. Research indicates that physical contact can activate neural pathways related to social needs, underscoring its importance in maintaining emotional bonds. In experimental settings, animals, including humans, show a preference for tactile stimulation, reinforcing the idea that touch is essential for fulfilling social desires and fostering healthy relationships.
How does social behavior relate to mental health and social connection neuroscience?
Social behavior is intricately linked to mental health, as neuroscience explores how our brains regulate the need for social engagement. The study of social connection neuroscience reveals that fulfilling social needs can mitigate feelings of isolation, thus improving mental health outcomes. Understanding these connections helps in devising interventions for mental health conditions affected by social deficits.
What are the long-term effects of social isolation on health according to neuroscience?
Long-term social isolation has been shown to adversely affect health, with neuroscience providing insights into these consequences. Prolonged isolation can lead to changes in brain function, reduced emotional regulation, and increased vulnerability to mental illness. This highlights the critical need for social connections to promote mental and physical health over time.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Social Connection as a Need | Health professionals recognize social connection as crucial, similar to food and shelter. |
| Public Health Concerns | The U.S. Surgeon General identified social isolation as a significant public health issue in 2023. |
| Research Insight | A new study reveals the brain mechanisms behind social needs, drawing parallels to hunger and thirst. |
| Hypothalamus Role | Researchers focused on the hypothalamus, identifying neurons activated during isolation that signify social need. |
| Touch Importance | Experiments show that physical touch is critical for fulfilling social needs, similar to human interactions. |
| Impact on Mental Health | Understanding social connection neuroscience can enhance comprehension of mental health issues like autism and depression. |
Summary
Social connection neuroscience is crucial in understanding the fundamental human need for social interactions, revealing how our brains regulate the desire to connect with others. The research highlights the parallels between social needs and basic physiological drives such as hunger and thirst, providing insights into the importance of social connections for mental and physical health. As the world becomes increasingly digital, these findings underscore the significance of maintaining tactile, real-world interactions to support emotional well-being.