Is sugar addictive? This question has stirred considerable debate in recent years, particularly as society grapples with rising sugar cravings and the pervasive presence of processed foods in our diets. While many people experience intense urges for sweet treats and may find it hard to resist sugary snacks, understanding the health effects of sugar is crucial. Unlike substances like alcohol or nicotine, which are officially classified as addictive, sugar’s role in our diets presents a complex picture. It may not fit the strict clinical definitions of addiction, but the compulsive patterns related to high sugar consumption can have significant implications for our health.
Exploring the concept of sugar as a potential contributor to dependency may redefine how we view our relationship with dietary sweets. Some nutrition experts suggest that the allure of sweet-tasting foods, often found in ultra-processed items, prompts cravings that can feel overwhelming. When discussing the psychological and physical impacts, it’s crucial to differentiate sugar from traditional addictive substances, as the consequences and removal from our lives vary significantly. Sugar intake is an integral part of our nutrition, present in natural foods alongside added sugars that often lead to unhealthy eating behaviors. Therefore, recognizing the nuances between healthful sweetness and harmful bingeing could empower individuals to make more informed dietary choices.
Understanding Sugar Cravings and Their Effects
Sugar cravings are a common experience for many, often triggered by the highly palatable nature of processed foods. These foods frequently contain not only added sugars but also unhealthy fats and sodium, making them remarkably attractive and hard to resist. The consumption of these ultra-processed foods can lead to habitual eating patterns, where the body begins to expect and crave the quick energy that sugar provides. Nutritionists emphasize that such cravings can become problematic, particularly when people rely heavily on sugary snacks and beverages to satisfy their dietary needs.
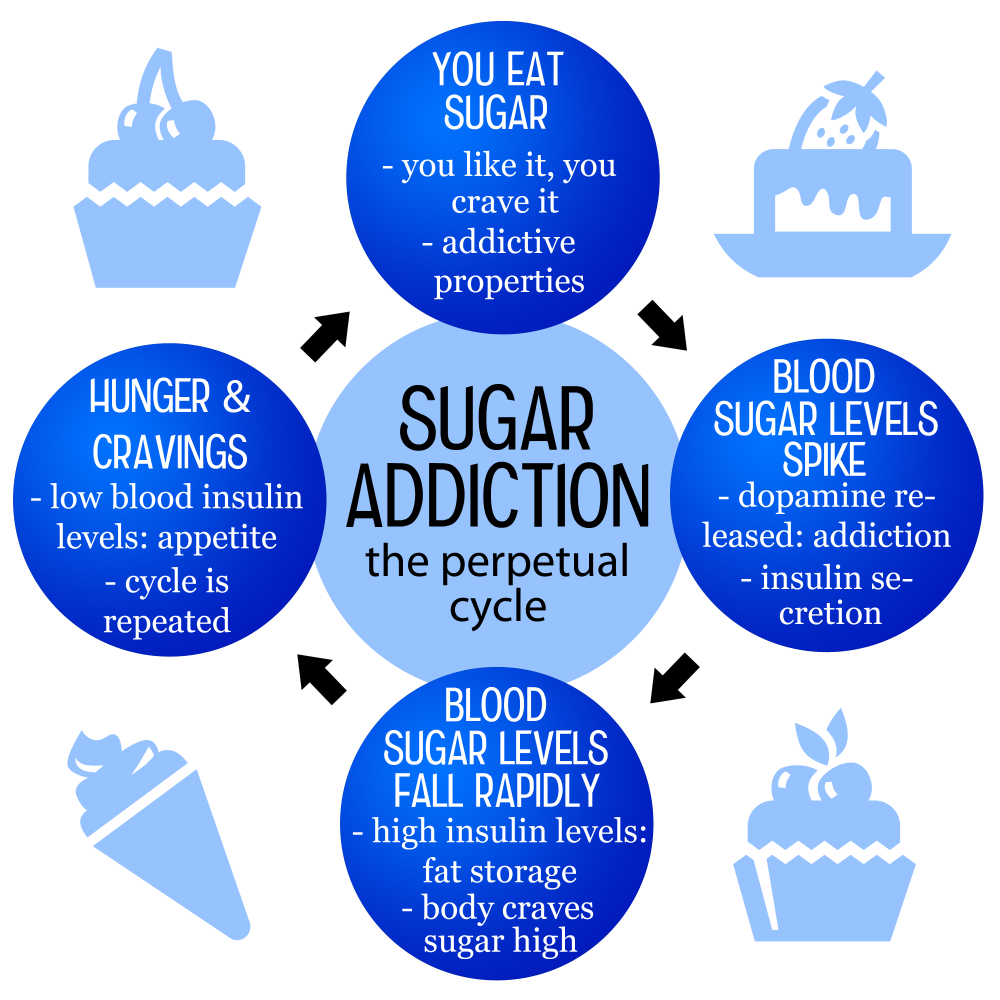
Moreover, the psychological aspects of sugar cravings cannot be ignored. When individuals cut down on sugar abruptly, they may experience withdrawal-like symptoms such as headaches and fatigue, similar to those faced when quitting more traditionally addictive substances. This has led to ongoing debates among researchers about whether sugar should be classified alongside alcohol, nicotine, and other addictive substances. While it has been established that sugar can influence cravings, distinguishing between necessary dietary nutrients and substances that are detrimental to health is crucial.
Is Sugar Addictive? A Closer Look
The question of whether sugar is addictive reflects a broader inquiry into the nature of cravings and consumption patterns in the modern diet. Unlike substances such as nicotine or alcohol, sugar does not meet the stringent clinical definitions of addiction; however, its effects on the brain may mimic those of addictive substances. As noted by nutrition experts, sugar can trigger neurochemical reactions that enhance pleasure, leading to a cycle of overconsumption. This relationship is particularly evident in individuals who frequently consume high amounts of sugar, raising concerns about the health effects of ongoing excessive intake.
It’s also important to recognize that not all sugar is created equal. Natural sugars found in fruits, vegetables, and dairy contribute essential nutrients and are necessary for bodily functions, while added sugars, commonly found in processed foods, pose significant health risks. Moderation is key; enjoying sweet flavors in a balanced diet yields benefits without the dangers of addiction. The American Heart Association recommends strict limits on added sugars, promoting awareness of consumption habits and encouraging gradual reduction over cold-turkey approaches, which could lead to a backlash in cravings.
Processed Foods and Sugar’s Role in Nutrition
In today’s food environment, ultra-processed foods have become ubiquitous. These products often contain high levels of added sugars, designed to enhance flavor and improve consumer appeal. Unfortunately, this not only satisfies immediate cravings but also creates a feedback loop that encourages further consumption. For many, this seems like an unbreakable cycle, as these foods offer quick gratification but may lead to long-term health consequences, including obesity and metabolic disorders.
Understanding the role of sugar in these foods is vital. By reading labels and becoming conscious of sugar intake, individuals can start making healthier choices that prioritize whole foods over processed alternatives. This shift toward a more natural diet can mitigate some of the cravings that are exacerbated by the high sugar content found in many snacks and drinks, ultimately leading to improved overall health and wellbeing.
The Health Effects of Sugar Moderation
The health implications of sugar consumption have come under increasing scrutiny, particularly as average daily intake continues to rise. With recommendations highlighting significantly lower consumption limits, knowing the sources and amounts of sugar we ingest is essential for maintaining a healthy lifestyle. Excessive sugar intake is linked to numerous health issues, including heart disease, diabetes, and dental problems, making awareness and moderation a paramount concern for health professionals.
Moderate sugar intake, however, should not be demonized; it plays a role in enhancing the flavor and enjoyment of healthy meals. Balancing sweet foods within our diets, while being mindful of the quantities consumed, can help maintain a satisfying lifestyle without falling into the traps of excessive cravings and emotional eating. Engaging with nutrition education can empower individuals to make informed decisions about their diet and establish healthier patterns.
Coping Strategies for Sugar Cravings
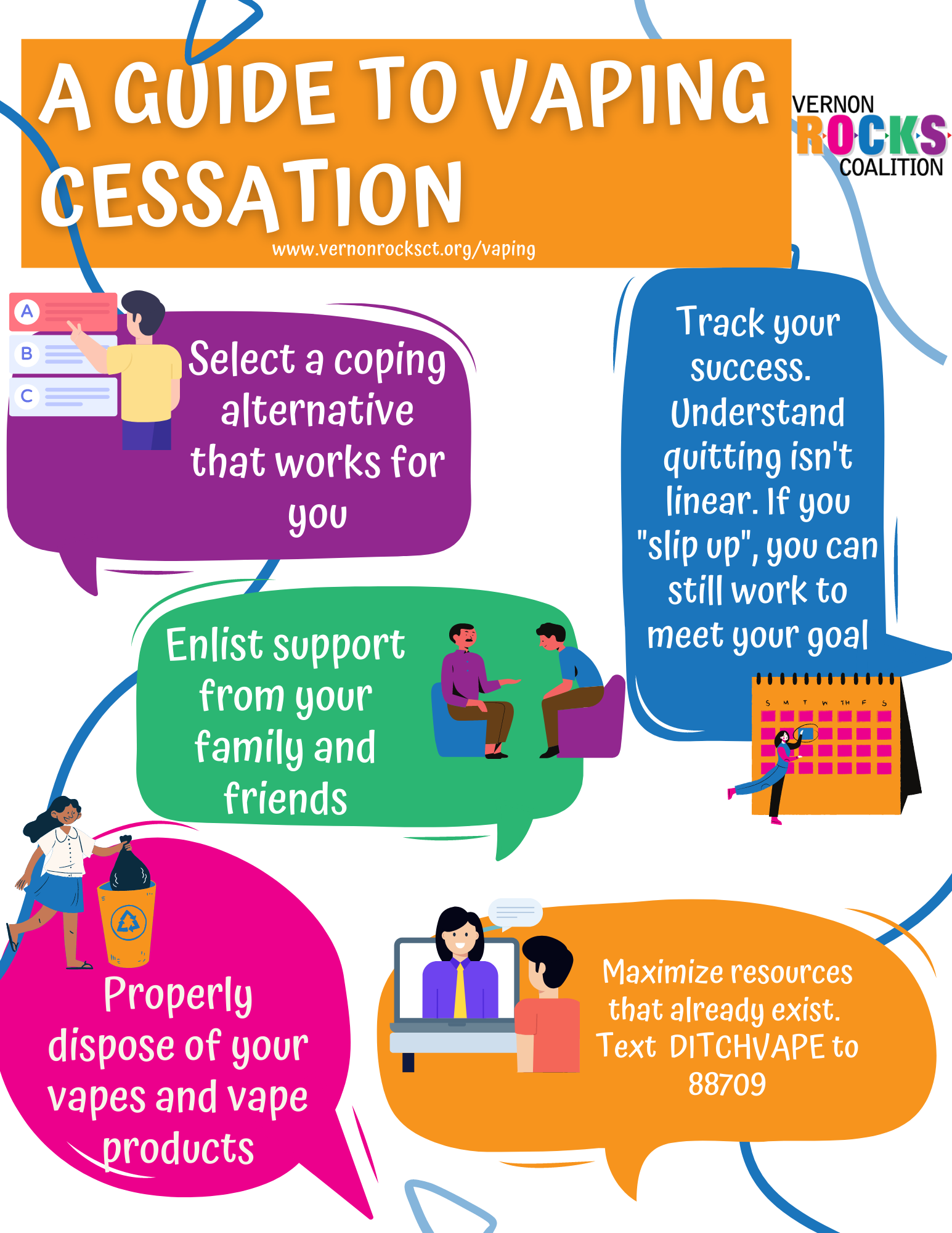
When faced with sugar cravings, effective coping strategies can make a significant difference in dietary habits. Experts recommend first acknowledging the craving without guilt, understanding that such feelings are normal. Incorporating alternative strategies can help manage those cravings more effectively. For instance, substituting sugary snacks with naturally sweet options like fruits can provide satisfaction while delivering essential nutrients, reducing the urge to revert to processed treats.
Another helpful approach is to focus on balanced meals that include proteins and healthy fats, as these can stabilize blood sugar levels and minimize impulsive sugar consumption. Staying hydrated is also critical; sometimes, cravings can stem from dehydration rather than true hunger. By creating healthier eating environments and planning meals ahead of time, individuals can reduce the impact of those occasional sugar cravings and foster a more sustainable relationship with food.
The Role of Education in Sugar Awareness
Education about sugar and its effects is crucial for developing better dietary practices. Understanding the distinctions between natural sugars and added sugars can empower individuals to make informed choices while shopping and cooking. Nutrition programs and public health campaigns play an important role in disseminating such information, highlighting the need to read food labels and be aware of hidden sugars present in many everyday products.
Furthermore, fostering a community of awareness can be beneficial; discussing these topics openly encourages individuals to share experiences, learn from one another, and hold each other accountable for healthier choices. By cultivating knowledge and awareness about sugar and dietary habits, we can collectively work towards reducing reliance on processed foods and enhance overall health outcomes.
The Psychological Factors Behind Sugar Consumption
The psychological dimensions of sugar consumption are an area of significant interest among researchers and health professionals. Many individuals turn to sugary foods for comfort or as a reward, establishing a psychological link that can perpetuate cravings. This cycle of emotional eating, where sugars are viewed as coping mechanisms for stress or sadness, complicates efforts to reduce sugar intake and can lead to increased dependence on sweet foods.
Addressing the emotional ties to sugar consumption often requires a holistic approach that includes psychological support and behavioral strategies. Mindfulness practices, for example, can help individuals recognize and manage cravings more effectively, differentiating between physical hunger and emotional needs. By developing healthier coping strategies and understanding the roots of these cravings, it becomes easier to establish a balanced relationship with sugar.
Sugar Reduction: A Practical Approach for Healthier Living
Reducing sugar in one’s diet doesn’t need to feel overwhelming or restrictive. In fact, a gradual approach is recommended by health professionals. Instead of eliminating sugar entirely, individuals can start by reducing the amounts in their coffee or tea, opting for unsweetened beverages, and choosing snacks that are naturally sweet or minimally processed. This piecemeal strategy can help ease the transition while still allowing enjoyment of sweet flavors in moderation.
Engaging with a supportive community or seeking professional advice can further facilitate this change. Whether it’s joining a nutrition group, working with a dietitian, or participating in cooking classes, having resources and support can reinforce new habits. Ultimately, the goal is to create a sustainable and enjoyable eating pattern that includes occasional indulgences while prioritizing overall health.
Exploring Natural Sources of Sugar
Natural sources of sugar, such as fruits and certain dairy products, provide essential nutrients in addition to sweetness. Unlike added sugars in processed foods, natural sugars come with fiber, vitamins, and minerals that contribute to overall health. For example, the fiber in fruits and whole grains not only aids digestion but also helps slow the absorption of sugars, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels.
Incorporating more naturally sweet foods into one’s diet can help satisfy those cravings without the negative health effects associated with added sugars. Experimenting with recipes that utilize fruits for sweetness or choosing products that are minimally processed can offer delicious alternatives. This shift not only improves nutrient intake but also fosters a healthier appreciation for natural flavors.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is sugar addictive like alcohol or nicotine?
While sugar can induce cravings similar to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive by clinical standards. Unlike alcohol and nicotine, which can cause severe withdrawal symptoms, sugar’s effects are more about habitual consumption linked to processed foods.
What causes sugar cravings and are they a sign of addiction?
Sugar cravings arise from the palatability of processed foods high in sugar, fats, and sodium. Although they may mimic addictive behaviors, these cravings are more about dietary habits than true addiction.
How does sugar in our diet relate to addictive substances?
Sugar can have addictive-like qualities, leading to compulsive eating and cravings; however, it is fundamentally different from substances like drugs or alcohol, as sugar is a necessary nutrient found naturally in many foods.
What are the health effects of sugar consumption?
Excessive sugar consumption is linked to various health issues, including obesity and metabolic disorders. The American Heart Association recommends limiting added sugars to reduce potential health risks.
How can I manage sugar cravings without feeling deprived?
Gradual reduction of added sugars in your diet can help manage cravings. Cutting sugar completely often leads to withdrawal-like symptoms, so it’s better to decrease intake slowly while focusing on whole foods.
Are processed foods more likely to trigger sugar cravings?
Yes, processed foods often contain high levels of added sugars, unhealthy fats, and sodium, which can intensify sugar cravings and lead to habitual consumption, contributing to unhealthy eating patterns.
What distinguishes sugar from other addictive substances?
The key difference is that sugar is a necessary component of our diet found in many essential foods, whereas substances like nicotine and alcohol can be completely eliminated without health consequences.
Can I still enjoy sugar without becoming addicted?
Yes, consuming sugar in moderation is perfectly fine. The focus should be on balanced dietary choices and understanding the difference between healthy sugars found in whole foods and added sugars in processed foods.
| Key Points | Details |
|---|---|
| Is Sugar Addictive? | While sugar can trigger cravings akin to addictive substances, it is not classified as addictive like alcohol or nicotine. The psychological and physical effects of sugar consumption can resemble withdrawal symptoms when reducing intake, but the severity is less than that of drugs. |
| Cravings and Compulsive Eating | Foods high in processed sugar also contain unhealthy fats and sodium, making them very palatable and increasing cravings. Habitual consumption can lead to addiction-like behaviors. |
| Sugar in Diets | Sugar is essential in moderation and is found in various healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, and dairy. It’s necessary for flavor and satisfaction in foods. |
| Recommended Sugar Intake | The American Heart Association suggests limiting added sugar to 9 teaspoons for men, 6 for women, and less for children, as the average American consumes about 20 teaspoons daily. |
| Gradual Reduction | Going ‘cold turkey’ on sugar can lead to backlash. A gradual decrease in added sugars in one’s diet is recommended for better adjustment. |
Summary
Is sugar addictive? This question has sparked considerable debate in nutrition and public health, mainly because while sugar does influence cravings and offers pleasurable experiences, it does not meet the strict clinical criteria for addiction like substances such as nicotine and alcohol. Understanding the nuances of sugar’s effects on our bodies and behavior is crucial, especially in a world where processed foods dominate our diets. Awareness of our sugar intake and approaching sugar consumption with balance and moderation can help mitigate potential negative impacts on health.