Antibiotic resistance has emerged as one of the most pressing health challenges of our era, threatening to undermine decades of medical advancements. This phenomenon occurs when bacteria evolve mechanisms to resist the effects of drugs that once successfully eradicated them, leading to an increase in drug-resistant infections. As the World Health Organization indicated, antibiotic resistance was responsible for over one million deaths worldwide in 2019 alone. With the limited approval of new antibiotics in recent years, innovative solutions are desperately needed to combat this growing crisis. Emerging biotechnology companies like Kinvard Bio are stepping up to address these challenges by developing new classes of antibiotics that target the bacterial ribosome, aiming to provide effective treatments for infections resistant to current therapies.
The crisis of antimicrobial resistance represents a significant threat to public health, impacting the efficacy of treatments for infectious diseases globally. As bacteria adapt and develop resistance to standard drugs, healthcare providers face increasing challenges in managing common infections. This growing issue highlights a crucial need for the development of novel bactericidal agents to restore the effectiveness of antibiotic therapies. The innovative efforts of organizations dedicated to creating new antimicrobial options, such as Kinvard Bio, are essential to overcoming the barriers posed by drug-resistant pathogens. As we strive to address this multifaceted problem, understanding the mechanisms of resistance and the importance of advancing antibiotic discovery becomes paramount.
Understanding Antibiotic Resistance and Its Global Impact
Antibiotic resistance is rapidly emerging as one of the most critical public health challenges that the world faces today. With the overuse and misuse of antibiotics, many bacterial infections that were once easily treatable have become increasingly difficult, if not impossible, to manage. The World Health Organization estimates that antibiotic resistance was responsible for over one million deaths worldwide in 2019 alone, highlighting the urgent need for new interventions. This situation threatens not only individual health outcomes but also the effectiveness of medical procedures that rely on antibiotics, such as surgeries and chemotherapy.
On a global scale, antibiotic resistance results in prolonged hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality. As pathogens evolve, they develop mechanisms to evade the effects of existing antibiotics, rendering many current treatment protocols ineffective. The rise of these drug-resistant infections signals an impending public health crisis that necessitates immediate action from scientists, healthcare providers, and policymakers alike. Solutions, such as the development of new antibiotics, are essential to combatting this pressing issue.
Kinvard Bio: Innovating the Future of Antibiotics
Amidst the alarming rise of antibiotic resistance, Kinvard Bio stands out as a pioneering biotechnology company determined to revolutionize antibiotic treatments. Founded in the prestigious Myers Lab at Harvard University, Kinvard Bio focuses on creating a novel class of antibiotics aimed at effectively treating drug-resistant infections. Their innovative approach revolves around targeting the bacterial ribosome, an essential component in the protein synthesis of bacteria. By developing compounds that bind with high affinity to the ribosome, Kinvard Bio aims to circumvent the existing resistance mechanisms that pathogens employ.
The lead compounds developed by Kinvard Bio, known as oxepanoprolinamides, are structurally optimized to enhance their effectiveness against a broad range of pathogens. This new strategy is particularly significant considering the current lag in antibiotic approvals, with an alarming decrease in new antibiotic classes available to combat infections. Kinvard Bio’s emphasis on synthesizing and testing molecules that are different from conventional antibiotics represents a crucial step in addressing the crisis of antimicrobial resistance. With promising early results from preclinical studies, there is hope that these new antibiotics can lead to better health outcomes for patients with severe bacterial infections.
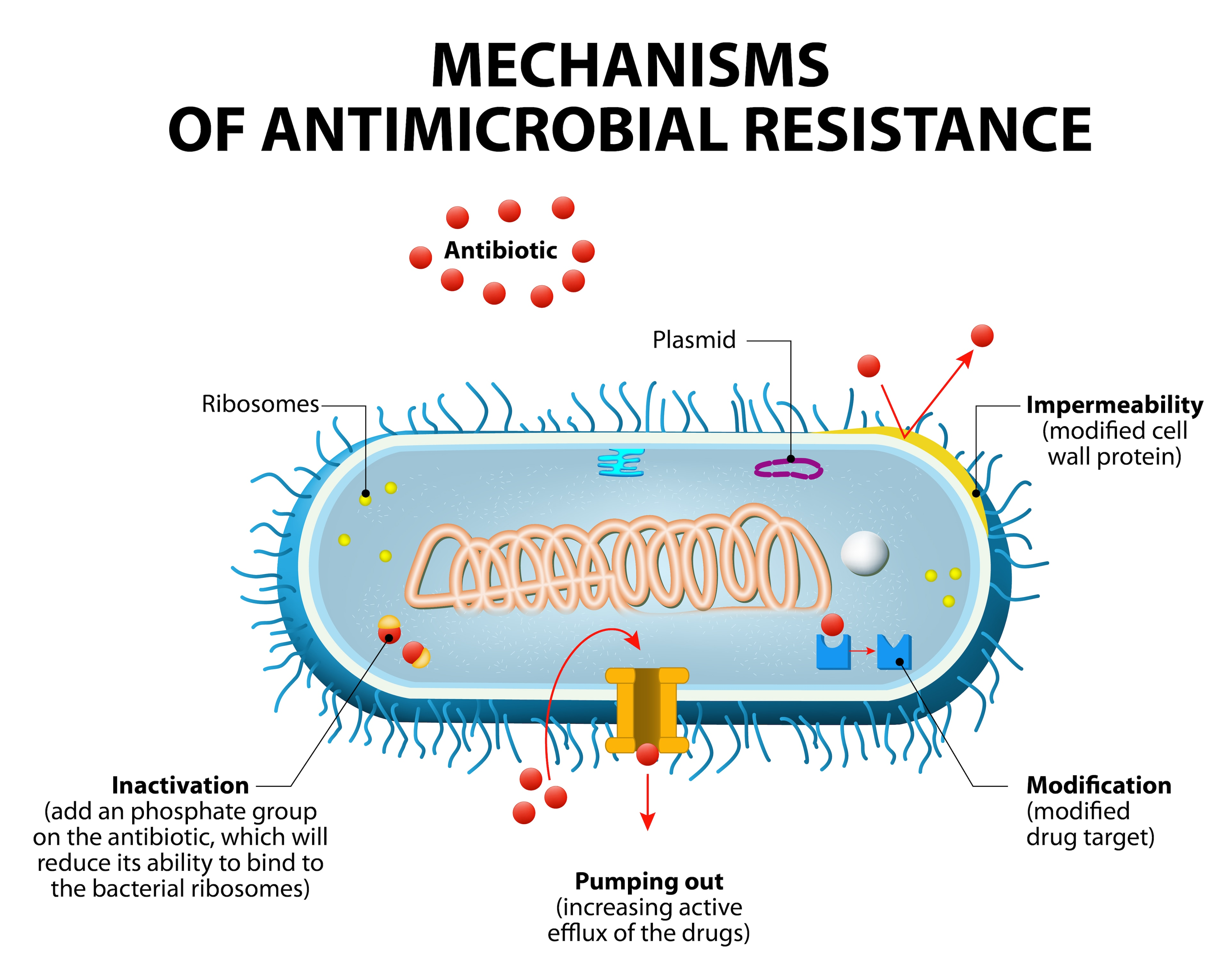
The Role of the Bacterial Ribosome in Antibiotic Development
The bacterial ribosome presents a validated and strategic target for the development of new antibiotics, particularly in the face of rising antibiotic resistance. This molecular machinery is crucial for protein synthesis in bacteria, and its disruption can effectively hinder bacterial growth and replication. By developing antibiotics that target the ribosome, Kinvard Bio seeks to provide a reliable approach to treat infections that have become resistant to existing antibacterial agents. This highly clinically validated target has seen a resurgence of interest, as researchers like those at Kinvard Bio explore new binding mechanisms that enable antibiotics to remain effective against resistant strains.
Moreover, the ability of Kinvard Bio’s oxepanoprolinamides to bind to the bacterial ribosome in a highly differentiated way may allow these new antibiotics to evade prevalent resistance pathways. As the lab continues to innovate and expand its research, the potential for these novel compounds to transform the way we approach drug-resistant infections grows. By leveraging synthetic chemistry, Kinvard Bio not only aims to develop potent new antibiotics but also to navigate the complexities of antimicrobial resistance in a pragmatic and effective manner.
The Importance of Collaboration in Combating Antimicrobial Resistance
Collaboration is essential in addressing the multifaceted challenge of antimicrobial resistance. Kinvard Bio exemplifies this through its partnerships with significant funding institutions like CARB-X and the Blavatnik Biomedical Accelerator. By harnessing collaborative resources, Kinvard Bio is positioned to accelerate the development of its antibiotic candidates and ultimately bring them to clinical trials. These partnerships enhance research capabilities by combining expertise, funding, and innovative technology, fostering an environment conducive to tackling some of the most pressing healthcare challenges.
Furthermore, working in conjunction with investors and other biotech firms creates a robust ecosystem that encourages the continual growth of new ideas and solutions. In the context of antibiotic development, such collaboration can lead not only to more effective treatments against drug-resistant infections but also to faster delivery of these therapies to the patients who need them the most. As Kinvard Bio forges ahead with its research, the integration of diverse scientific insights and collaborative efforts will be pivotal in overcoming the hurdles posed by antimicrobial resistance.
Exploring New Antibiotic Classes to Combat the Resistance Crisis
The urgent need for innovative solutions in the field of antibiotics is pressing, particularly given the alarming statistics surrounding antibiotic resistance. The conventional pipeline for developing new antibiotics has stagnated, with few new classes emerging in recent years, highlighting a gap in effective treatments for resistant infections. Kinvard Bio is stepping into this void by exploring new classes of antibiotics that diverge from existing drugs, thereby providing hope in the battle against drug-resistant bacteria. Their ongoing research into these innovative compounds reflects a commitment to expanding the arsenal against antibiotic-resistant pathogens.
The shift towards developing entirely new antibiotic classes is critical, as traditional antibiotics lose efficacy due to resistance mechanisms. Kinvard Bio’s focus on innovative approaches enables the disruption of established resistance pathways. By capitalizing on cutting-edge synthetic chemistry and rigorous testing, the company aims to redefine how antibiotics combat infections. This transition from traditional methods to novel solutions promises to rejuvenate the fight against drug-resistant infections, offering a new lease on life for patients worldwide.
The Future of Antibiotic Discovery: A Collaborative Approach
The future of antibiotic discovery lies in a collaborative approach that brings together researchers, healthcare professionals, and institutions. Kinvard Bio embodies this philosophy by leveraging the expertise of Professor Andrew Myers and his lab at Harvard University. The collaborative nature of Kinvard Bio’s formation underscores the importance of pooling resources and knowledge in addressing the complexities of antimicrobial resistance. By fostering collaboration, the company not only improves the likelihood of successful drug development but also creates a path for a new generation of scientists dedicated to combating this critical issue.
Additionally, engaging with interdisciplinary networks enhances research capabilities, as different perspectives fuel innovation. For Kinvard Bio, collaborations extend beyond academic circles to include industry partners who recognize the urgency of the antimicrobial resistance crisis. Such alliances foster a shared commitment towards the urgent development of effective antibiotics, essential for managing current and emerging health threats. The promise of a healthier future hinges on harnessing the power of collaboration to navigate the intricacies of antibiotic resistance together.
The Role of Synthetic Chemistry in New Antibiotic Development
Synthetic chemistry plays an integral role in the development of new antibiotics, providing the necessary tools to innovate and create effective treatment options. Kinvard Bio’s research emphasizes the application of synthetic chemistry to design and produce novel compounds that target drug-resistant bacteria. By employing sophisticated chemical synthesis techniques, researchers can engineer molecules that are optimized for binding to specific bacterial targets, such as the ribosome.
This approach not only maximizes the potential efficacy of new antibiotics but also allows for the exploration of chemical structures that may circumvent existing bacterial resistance mechanisms. Kinvard Bio’s commitment to pioneering synthetic chemistry ultimately contributes to the discovery process, offering the potential to transform how we treat infectious diseases and address the pervasive challenge of antimicrobial resistance.
Addressing Acute and Chronic Infections with New Antibiotics
As Kinvard Bio progresses in developing its new antibiotics, it is strategically targeting both acute and chronic infections that pose significant health risks to patients. Conditions such as bacterial pneumonia and complicated urinary tract infections require urgent treatment options due to their potential severity and the increasing prevalence of drug-resistant strains. Kinvard Bio’s focus on these high-need areas allows for meaningful impact in clinical settings, particularly as healthcare systems face the burden of rising healthcare costs and prolonged hospitalization.
In addition to acute infections, Kinvard Bio’s pipeline may eventually extend to treating chronic conditions, such as nontuberculous mycobacteria lung disease, which present unique challenges to clinicians. By addressing these varied types of infections, Kinvard Bio enhances the potential for better patient outcomes and decreases the overall strain on healthcare resources. Implementing new antibiotics effectively into treatment regimens can not only save lives but also improve quality of life for individuals battling chronic infections, marking a significant step forward in the fight against antibiotic resistance.
The Importance of Clinical Trials in Antibiotic Development
Clinical trials represent a critical phase in the development of new antibiotics, providing essential data on their safety and efficacy before they reach the market. For Kinvard Bio, progressing its antibiotic candidates into human clinical trials is a key priority, as it validates the innovative approaches taken during the research and development phases. Clinical trials are integral to demonstrating the effectiveness of new treatments against drug-resistant infections, often leading to significant improvements in patient care.
Moreover, the insights gained from clinical trials can influence subsequent research directions and optimize therapeutic strategies. As antibiotic resistance continues to escalate, the need for robust clinical data becomes even more pronounced, allowing healthcare providers to make informed decisions when treating complicated infections. Kinvard Bio’s commitment to rigorous clinical testing ensures that its new antibiotics are not only groundbreaking in their design but also effective in real-world patient scenarios.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is antibiotic resistance and why is it important?
Antibiotic resistance refers to the ability of bacteria to evolve and withstand the effects of antibiotics, making them ineffective in treating infections. This growing crisis is important because it contributes to increased mortality and complications in treating drug-resistant infections, which the World Health Organization links to millions of deaths globally. Understanding antibiotic resistance is crucial for developing new treatments and combating this public health challenge.
How are new antibiotics being developed to combat antibiotic resistance?
New antibiotics are being developed by biotechnology companies like Kinvard Bio, which focuses on creating innovative compounds that target the bacterial ribosome, a clinically validated site for antibiotic action. By designing antibiotics, such as oxepanoprolinamides, that bind differently to the ribosome, researchers aim to overcome existing resistance mechanisms and ensure effective treatment against drug-resistant infections.
What role does Kinvard Bio play in addressing antibiotic resistance?
Kinvard Bio is a biotechnology startup that aims to combat antibiotic resistance by developing a new class of antibiotics specifically designed to target bacterial ribosomes. Their innovative compounds, which have shown potential in preclinical studies, are focused on treating infections caused by drug-resistant pathogens, thereby contributing to the ongoing fight against antimicrobial resistance.
Why is the bacterial ribosome a key target in the fight against antibiotic resistance?
The bacterial ribosome is a crucial target in addressing antibiotic resistance because it is essential for protein synthesis in bacteria. Many established antibiotics focus on this target, but new compounds, like those developed by Kinvard Bio, aim to bind to the ribosome in a unique way that circumvents existing resistance mechanisms, offering hope for effective treatment against resistant bacteria.
What are the implications of antimicrobial resistance on public health?
Antimicrobial resistance poses severe implications for public health, leading to longer hospital stays, higher medical costs, and increased mortality rates. As antibiotics become less effective, treating common infections becomes more complicated and can result in a return to pre-antibiotic era challenges, making the development of new antibiotics essential for modern medicine.
Can new antibiotics reduce the prevalence of drug-resistant infections?
Yes, the development of new antibiotics, like those being created by Kinvard Bio, has the potential to significantly reduce the prevalence of drug-resistant infections. By specifically targeting resistant pathogens and employing innovative binding mechanisms, these new drugs can restore the efficacy of antibiotic treatments, leading to better patient outcomes and reducing the burden of antimicrobial resistance.
How are new antibiotic compounds approved and tested for effectiveness against drug-resistant infections?
New antibiotic compounds undergo rigorous testing and clinical trials to assess their safety and effectiveness before receiving approval. Companies like Kinvard Bio conduct preclinical studies to demonstrate activity against specific pathogens, and once promising results are achieved, they progress to human clinical trials, monitored by regulatory authorities such as the FDA.
What is the significance of the research conducted at Harvard University regarding antibiotic resistance?
The research at Harvard University, particularly in the Myers Lab, is significant as it focuses on innovating new classes of antibiotics to tackle the urgent issue of antibiotic resistance. With substantial funding and a dedicated team, this research aims to produce viable new treatments that can effectively fight drug-resistant infections, thus addressing a critical need in global health.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Antibiotic Resistance Challenge | Antibiotic resistance is a major global health crisis leading to over 1 million deaths annually. |
| History of Antibiotics | Penicillin was the first antibiotic, revolutionizing medicine since the 1940s. |
| New Antibiotic Development | Between 2017 and 2022, only 12 new antibiotics were approved, highlighting the urgency for innovation. |
| Kinvard Bio’s Initiative | A startup focused on creating new antibiotics, particularly targeting drug-resistant infections. |
| Focus on Ribosome Targeting | Kinvard Bio’s antibiotics bind to the bacterial ribosome, offering potential resistance avoidance. |
| Research and Funding | Supported by various funding sources, including CARB-X, to tackle antibiotic resistance. |
| Future Developments | Initial focus on infections like bacterial pneumonia, with potential expansion to chronic illnesses. |
Summary
Antibiotic resistance continues to be a critical challenge in modern medicine, with profound implications for health worldwide. The urgent need for innovative solutions is exemplified by the efforts of startups like Kinvard Bio, which is dedicated to developing a new class of antibiotics capable of combating drug-resistant infections. Their research not only aims to create more effective treatments but also fosters a new generation of scientists focused on addressing this ongoing health crisis.